You know that your parts require some kind of non-destructive testing inspection, but do you know what is happening to your parts when that test method is applied? Over the next few weeks, our level III technicians will provide an explanation of each NDT method we employ along with some advantages and limitations of each.
For the last post of our series, we will discuss Wire Rope testing. We hope you have found this blog series to be interesting and informative!
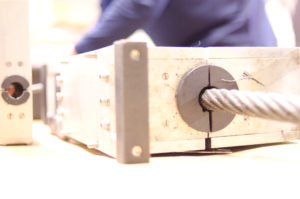 Wire rope testing is a form of electromagnetic inspection using equipment designed specifically for steel braided wire rope. Steel rope is used in a variety of applications such as amusements parks, mine shafts, suspension bridges and overhead cranes.
Wire rope testing is a form of electromagnetic inspection using equipment designed specifically for steel braided wire rope. Steel rope is used in a variety of applications such as amusements parks, mine shafts, suspension bridges and overhead cranes.
The equipment utilizes two strong magnets in a clam shell type set up to clamp around the rope. These magnets create a constant magnetic field in the steel rope. Since the magnetic field is constant, the amount of flux necessary to saturate the rope is a function of the cross-sectional area of the rope.
If the section of the rope that passes through the machine contains defects such as broken wires, corrosion thinning or stretching, the magnetic flux will be affected. These changes are interpreted on an oscilloscope display.
With proper calibration and training the technician can determine percentage of cross sectional loss, broken wires, and overall loss of break strength.
Contributed by:
Brian Bulgrin
Eddy Current & Ultrasonic Level III